Inflammation and Skin Aging: A Complex Relationship
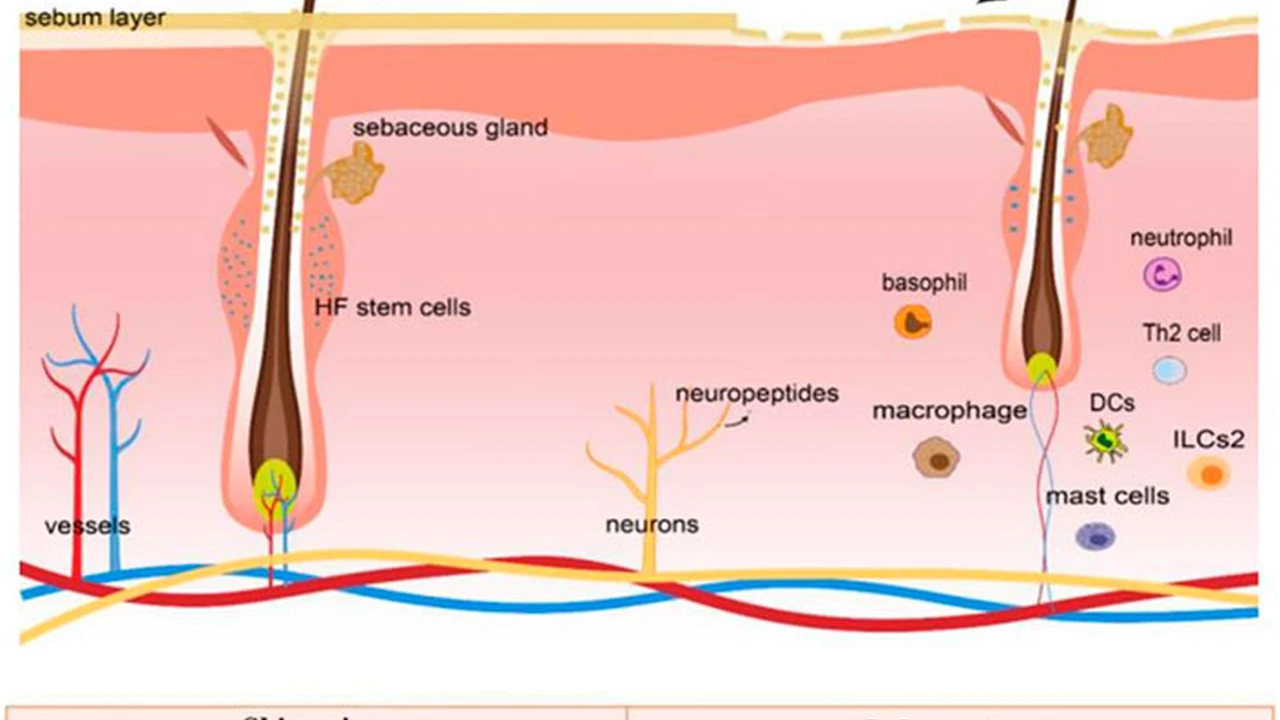
Understanding the Hallmarks of Aging A Comprehensive Overview
Aging, a multifaceted and intricate process, is characterized by a gradual decline in physiological functions, ultimately leading to increased susceptibility to disease and mortality. Deciphering the underlying mechanisms driving this decline is paramount to developing effective anti-aging strategies. Several hallmarks of aging have been identified, each contributing to the overall aging phenotype. Let's delve into these key hallmarks:
Genomic Instability The Foundation of Cellular Decline
Genomic instability refers to the accumulation of DNA damage and mutations over time. This damage can arise from various sources, including oxidative stress, radiation exposure, and errors during DNA replication. As DNA integrity deteriorates, cells become less efficient at repairing damage, leading to further genomic instability. This cascade effect can disrupt gene expression, impair cellular function, and ultimately contribute to age-related diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Think of it like a building with cracks in its foundation; eventually, the entire structure becomes unstable.
Telomere Attrition The Shortening of Life's Fuse
Telomeres are protective caps located at the ends of chromosomes. They shorten with each cell division, acting as a biological clock. Once telomeres reach a critical length, cells enter a state of senescence or apoptosis (programmed cell death). While telomere shortening is a natural process, accelerated telomere attrition can be triggered by factors such as chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. Maintaining telomere length is considered a crucial aspect of healthy aging. Consider them like the fuse on a firework; the shorter the fuse, the sooner it will go off.
Epigenetic Alterations The Shifting Landscape of Gene Expression
Epigenetics involves modifications to DNA and its associated proteins (histones) that regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. These modifications can be influenced by environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle. Age-related epigenetic alterations can disrupt gene expression patterns, leading to cellular dysfunction and disease. Imagine epigenetics as the dimmer switches that control the brightness of different genes; as we age, these switches can malfunction, dimming the lights on essential genes or turning up the lights on genes that promote aging.
Loss of Proteostasis The Breakdown of Cellular Housekeeping
Proteostasis refers to the maintenance of protein homeostasis, ensuring that proteins are properly folded, modified, and degraded. As we age, the proteostasis network becomes less efficient, leading to the accumulation of misfolded and aggregated proteins. These protein aggregates can disrupt cellular function and contribute to age-related diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Think of proteostasis as the cellular housekeeping system; when it breaks down, cellular garbage accumulates, leading to dysfunction.
Deregulated Nutrient Sensing The Imbalance of Metabolic Pathways
Nutrient sensing pathways, such as the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway and the mTOR pathway, regulate cellular growth, metabolism, and survival in response to nutrient availability. Dysregulation of these pathways can contribute to aging. For example, chronic activation of the mTOR pathway can accelerate aging, while caloric restriction (CR) can extend lifespan by inhibiting mTOR signaling. Maintaining a balanced nutrient sensing system is crucial for healthy aging. Imagine nutrient sensing pathways as the cellular fuel gauges; when they malfunction, the engine can either run too hot (accelerated aging) or not get enough fuel (cellular dysfunction).
Mitochondrial Dysfunction The Powerhouse's Decline
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP. Mitochondrial dysfunction, characterized by decreased ATP production, increased oxidative stress, and impaired mitochondrial dynamics, is a hallmark of aging. Damaged mitochondria can contribute to cellular dysfunction and age-related diseases. Think of mitochondria as the cellular batteries; when they start to fail, the cell loses power and becomes less efficient.
Cellular Senescence The Zombie Cells of Aging
Cellular senescence is a state of irreversible cell cycle arrest. Senescent cells accumulate with age and secrete a variety of pro-inflammatory factors, collectively known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The SASP can promote inflammation, tissue damage, and age-related diseases. Clearing senescent cells has been shown to extend lifespan and improve healthspan in animal models. Think of senescent cells as zombie cells; they are no longer functional and secrete harmful substances that damage surrounding tissues.
Stem Cell Exhaustion The Depletion of Regenerative Capacity
Stem cells are responsible for tissue repair and regeneration. As we age, stem cell numbers and function decline, leading to impaired tissue repair and increased susceptibility to age-related diseases. Maintaining stem cell function is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and promoting healthy aging. Imagine stem cells as the cellular repair crew; when they are depleted, the body becomes less able to repair damage and maintain its structural integrity.
Altered Intercellular Communication The Breakdown of Cellular Harmony
Intercellular communication is essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis and coordinating cellular function. Age-related alterations in intercellular communication, such as changes in cytokine signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling, can disrupt tissue function and contribute to aging. Maintaining effective intercellular communication is crucial for ensuring that cells work together harmoniously. Think of intercellular communication as the cellular communication network; when it breaks down, cells become isolated and unable to coordinate their activities effectively.
Chronic Inflammation The Silent Killer
Chronic inflammation, also known as inflammaging, is a low-grade, systemic inflammation that increases with age. It is characterized by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6. Chronic inflammation can contribute to a variety of age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease. Reducing chronic inflammation is a key strategy for promoting healthy aging. Think of chronic inflammation as a smoldering fire; it slowly damages tissues over time, contributing to age-related diseases.
Targeting Aging with Cutting Edge Nutritional Supplements
While a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle are crucial for healthy aging, certain nutritional supplements can provide additional support by targeting specific hallmarks of aging. Let's explore some promising supplements and their potential benefits:
NMN Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Boosting NAD Levels for Cellular Energy
NMN is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial coenzyme involved in numerous cellular processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and gene expression. NAD+ levels decline with age, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular senescence. Supplementing with NMN can increase NAD+ levels, potentially improving energy metabolism, protecting against DNA damage, and promoting healthy aging. Use Cases: NMN is often used by individuals seeking to improve energy levels, enhance cognitive function, and support overall healthspan. It is particularly popular among athletes and individuals experiencing age-related decline in energy and vitality. Product Recommendation: Elysium Health Basis. Basis combines NMN with pterostilbene, a potent antioxidant, to further enhance its anti-aging effects. Details: Elysium Health Basis is a popular NMN supplement that has undergone clinical trials. It is available in capsule form and is typically taken daily. Pricing starts at around $50 per month for a subscription. Pros: Clinically studied, contains pterostilbene for added antioxidant benefits, reputable brand. Cons: Relatively expensive compared to some other NMN supplements. Alternative: Renue by Science Lipo NMN. This liposomal NMN formulation may offer enhanced absorption compared to standard NMN capsules. Pricing starts around $70 per bottle. Pros: Potentially better absorption, reputable brand, third-party tested. Cons: More expensive than standard NMN supplements, liposomal formulations can be more sensitive to storage conditions.
Resveratrol The Antioxidant Powerhouse for Longevity
Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol found in grapes, red wine, and certain berries. It is a potent antioxidant and has been shown to activate sirtuins, a family of proteins involved in regulating aging and longevity. Resveratrol may help protect against age-related diseases, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance cognitive function. Use Cases: Resveratrol is often used by individuals seeking to protect against oxidative stress, support cardiovascular health, and promote healthy aging. Product Recommendation: Thorne Research ResveraCel. ResveraCel combines resveratrol with nicotinamide riboside (NR), another NAD+ precursor, and betaine anhydrous to support cellular energy production and healthy aging. Details: Thorne Research is a reputable brand known for its high-quality supplements. ResveraCel is available in capsule form and is typically taken daily. Pricing starts at around $60 per bottle. Pros: Contains NR for synergistic effects, reputable brand, third-party tested. Cons: Relatively expensive, contains multiple ingredients, which may not be suitable for everyone. Alternative: BulkSupplements.com Resveratrol. This is a pure resveratrol powder that can be easily added to smoothies or other beverages. It is a more affordable option compared to branded supplements. Pricing starts around $20 per package. Pros: Affordable, pure resveratrol, versatile for mixing into beverages. Cons: Requires measuring dosages, may have a slightly bitter taste.
Curcumin The Anti Inflammatory Spice for Healthy Aging
Curcumin is the active compound in turmeric, a spice widely used in Indian cuisine. It is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant and has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including protecting against age-related diseases, improving cognitive function, and reducing joint pain. Use Cases: Curcumin is often used by individuals seeking to reduce inflammation, support joint health, and protect against age-related diseases. Product Recommendation: Thorne Research Meriva-SF. Meriva-SF is a patented form of curcumin that is highly bioavailable, meaning it is better absorbed by the body compared to standard curcumin extracts. Details: Thorne Research is a reputable brand known for its high-quality supplements. Meriva-SF is available in capsule form and is typically taken daily. Pricing starts at around $40 per bottle. Pros: Highly bioavailable, reputable brand, third-party tested. Cons: Relatively expensive compared to some other curcumin supplements. Alternative: Doctor's Best High Absorption Curcumin. This curcumin supplement contains BioPerine, a black pepper extract that enhances curcumin absorption. Pricing starts around $20 per bottle. Pros: Affordable, contains BioPerine for enhanced absorption. Cons: May not be as bioavailable as Meriva-SF.
CoQ10 Coenzyme Q10 Energizing Cells and Protecting Against Oxidative Stress
CoQ10 is a naturally occurring antioxidant that plays a crucial role in energy production within mitochondria. CoQ10 levels decline with age, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction and increased oxidative stress. Supplementing with CoQ10 can improve energy levels, protect against oxidative damage, and support cardiovascular health. Use Cases: CoQ10 is often used by individuals seeking to improve energy levels, support cardiovascular health, and protect against oxidative stress. It is particularly beneficial for individuals taking statin medications, which can deplete CoQ10 levels. Product Recommendation: Qunol Ultra CoQ10. Qunol Ultra CoQ10 is a patented form of CoQ10 that is highly bioavailable, meaning it is better absorbed by the body compared to standard CoQ10 supplements. Details: Qunol is a well-known brand specializing in CoQ10 supplements. Qunol Ultra CoQ10 is available in softgel form and is typically taken daily. Pricing starts around $30 per bottle. Pros: Highly bioavailable, well-known brand, easy to swallow softgels. Cons: Relatively expensive compared to some other CoQ10 supplements. Alternative: Doctor's Best High Absorption CoQ10. This CoQ10 supplement contains BioPerine, a black pepper extract that enhances CoQ10 absorption. Pricing starts around $15 per bottle. Pros: Affordable, contains BioPerine for enhanced absorption. Cons: May not be as bioavailable as Qunol Ultra CoQ10.
Pterostilbene The Resveratrol Cousin with Enhanced Bioavailability
Pterostilbene is a natural antioxidant found in blueberries and grapes. It is structurally similar to resveratrol but has better bioavailability, meaning it is more readily absorbed by the body. Pterostilbene may help protect against age-related diseases, improve cognitive function, and reduce inflammation. Use Cases: Pterostilbene is often used by individuals seeking to protect against oxidative stress, support cognitive function, and reduce inflammation. It is often taken in combination with resveratrol for synergistic effects. Product Recommendation: Jarrow Formulas Pterostilbene. Jarrow Formulas is a reputable brand known for its high-quality supplements. Their pterostilbene supplement is available in capsule form and is typically taken daily. Pricing starts around $25 per bottle. Pros: Reputable brand, affordable, well-researched. Cons: May not be as potent as some other antioxidants.
Lifestyle Interventions for Longevity and Rejuvenation
Beyond supplementation, adopting a healthy lifestyle is paramount for promoting longevity and rejuvenation. Let's explore some key lifestyle interventions:
Caloric Restriction Mimicking The Power of Fasting
Caloric restriction (CR), reducing calorie intake without causing malnutrition, has been shown to extend lifespan and improve healthspan in various organisms, including yeast, worms, flies, and rodents. CR can activate sirtuins, improve mitochondrial function, and reduce inflammation. While long-term CR can be challenging for humans, intermittent fasting (IF) and time-restricted feeding (TRF) are more sustainable approaches that can mimic some of the benefits of CR. Practical Tips: Start with a 12-hour eating window and gradually reduce it to 8 hours. Experiment with different IF protocols, such as the 5:2 diet (eating normally for 5 days and restricting calories for 2 days). Considerations: Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any CR or IF regimen, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Exercise The Fountain of Youth
Regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to promote healthy aging. It can improve cardiovascular health, strengthen bones and muscles, enhance cognitive function, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Both aerobic exercise (e.g., running, swimming, cycling) and resistance training (e.g., weightlifting) are beneficial. Practical Tips: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Incorporate resistance training exercises at least two days per week. Considerations: Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Stress Management Techniques for Inner Peace
Chronic stress can accelerate aging by increasing inflammation, impairing immune function, and disrupting hormonal balance. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress levels and promote healthy aging. Practical Tips: Dedicate at least 10-15 minutes each day to stress management practices. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you. Considerations: Be patient and consistent with your stress management practices. It may take time to see results.
Sleep Hygiene Prioritizing Rest and Recovery
Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining physical and mental health. Sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function, weaken the immune system, and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Practical Tips: Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimize your sleep environment. Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Considerations: Consult with a healthcare professional if you have difficulty sleeping.
The Future of Aging Research Emerging Therapies and Technologies
The field of aging research is rapidly evolving, with numerous promising therapies and technologies on the horizon. Let's explore some exciting areas of research:
Senolytics Targeting Senescent Cells for Rejuvenation
Senolytics are drugs that selectively kill senescent cells. Clearing senescent cells has been shown to extend lifespan and improve healthspan in animal models. Several senolytic drugs are currently being investigated in clinical trials for various age-related diseases. Examples: Dasatinib and quercetin, fisetin, navitoclax. Potential Benefits: Improved physical function, reduced inflammation, protection against age-related diseases.
Gene Therapy Editing The Blueprint of Life
Gene therapy involves modifying genes to treat or prevent disease. Gene therapy holds promise for correcting genetic defects that contribute to aging and age-related diseases. Examples: CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology. Potential Benefits: Correction of genetic defects, enhanced cellular function, prevention of age-related diseases.
Stem Cell Therapy Regenerating Tissues and Organs
Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Stem cell therapy has the potential to regenerate tissues and organs that have been damaged by aging or disease. Examples: Bone marrow transplantation, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Potential Benefits: Tissue regeneration, organ repair, improved physical function.
Artificial Intelligence Revolutionizing Aging Research
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to accelerate aging research by analyzing large datasets, identifying novel drug targets, and developing personalized interventions. Examples: Machine learning algorithms for predicting lifespan, AI-powered drug discovery platforms. Potential Benefits: Accelerated drug discovery, personalized interventions, improved understanding of aging mechanisms.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)